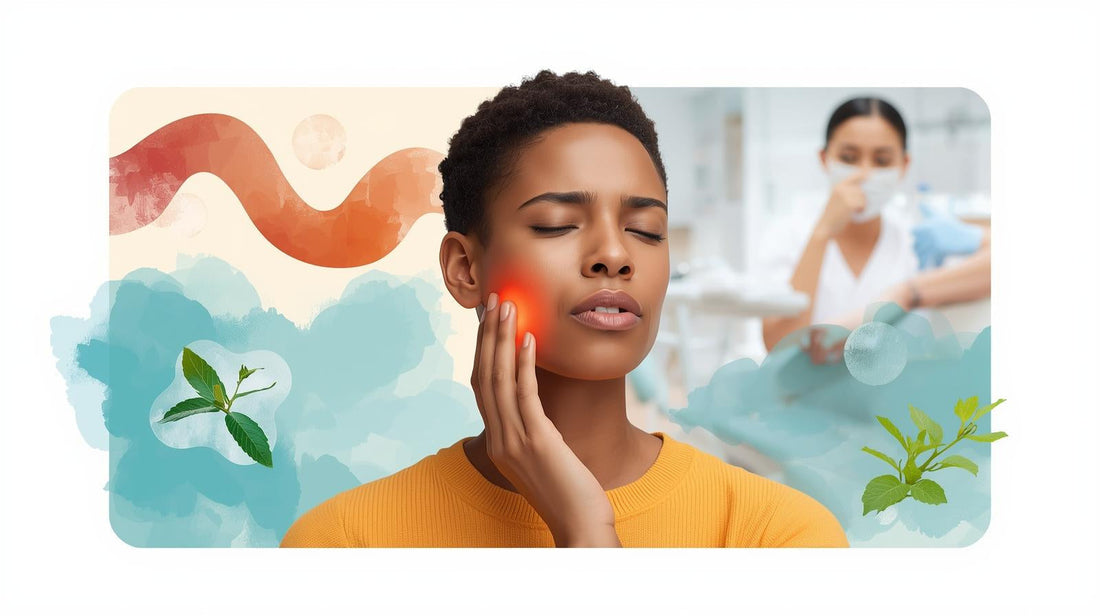
What Causes Chronic Jaw Pain and How to Treat It?
Share
Here’s the truth: chronic jaw pain isn’t one thing — it’s a mix of mechanical, muscular, lifestyle, and sometimes systemic issues.
This post will break down the real causes, how to figure out which one applies to you, and what treatments actually work (without wasting years chasing the wrong fix).
The Most Common Causes of Chronic Jaw Pain
Most cases fall into one or more of these categories:
-
Joint problems — issues with the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) itself.
-
Muscle overuse — from clenching, grinding, or poor posture.
-
Structural changes — arthritis, bone spurs, or injury.
-
Systemic conditions — autoimmune disorders, hormonal shifts, or chronic inflammation.
For a deep dive, read The Complete Guide to TMJ Disorders: Causes, Symptoms, and Solutions.
Internal Derangement of the Articular Disc Explained
Inside your jaw joint is a small cartilage disc.
When it slips out of place or degenerates, it can cause:
-
Clicking or popping sounds.
-
Pain with chewing.
-
Limited range of motion.
If ignored, it can progress to permanent joint damage.
Read more in What Are the Risks of Untreated TMJ?.
Myofascial Pain in TMJ – Symptoms and Remedies
This is essentially muscle knot pain in your jaw and surrounding muscles.
What helps:
-
Trigger point massage (masseter, temporalis, pterygoid muscles).
-
Warm compresses before bed.
-
Stretching and jaw relaxation exercises.
Get practical relief ideas in Best Home Remedies and Exercises for TMJ Pain Relief.
Can Osteoarthritis Cause TMJ Pain?
Yes — your jaw joint can develop arthritis just like knees or hips.
This can lead to stiffness, pain, and grinding sounds.
Learn more in Can Improving Bite Alignment Help with Back Pain? — the same mechanics often apply to jaw joints.
Trauma vs. Degeneration: Which Drives Jaw Pain?
-
Trauma — sudden impact, dental strain, whiplash.
-
Degeneration — slow wear from arthritis, bruxism, poor bite alignment.
For a breakdown, see TMJ vs. Stress: How to Tell the Difference.
Lifestyle Factors That Worsen Chronic Jaw Pain
You might be making it worse without knowing:
-
Chewing gum daily.
-
Leaning your head on your hand at your desk.
-
Eating hard, chewy foods often.
-
Sleeping on your stomach with head turned.
Medical Conditions Linked to TMJ Pain
Some health issues can amplify jaw pain:
-
Fibromyalgia.
-
Autoimmune disorders.
-
Chronic sinusitis.
-
Hormonal changes in women.
See TMJ in Women: Unique Challenges and Solutions for gender-specific insights.
Treatment Options for Chronic Jaw Pain
Think of treatment in layers:
-
Reduce inflammation — ice, anti-inflammatory diet.
-
Restore mobility — gentle exercises, physical therapy.
-
Protect the joint — custom TMJ appliances.
-
Address root cause — stress, posture, systemic illness.
Physical Therapy for Jaw Pain Management
A skilled TMJ physiotherapist can:
-
Improve mobility.
-
Release tight muscles.
-
Teach prevention habits.
See Holistic Approaches to TMJ: Beyond the Dentist’s Chair.
Role of Stress and Mental Health in Jaw Pain
Stress fuels clenching and inflammation.
What’s worked for me:
-
Box breathing.
-
Screen breaks.
-
Jaw relaxation reminders.
Read more in Stress, Anxiety, and Their Impact on TMJ.
When Is Surgery Needed for TMJ Pain?
Rarely — only for severe, unresolved cases.
If it’s offered as the first step, be cautious.
Learn about alternatives in Best Non-Invasive Alternatives to Jaw Surgery for Chronic Pain.
Medication Pros and Cons for Chronic TMJ
-
Pros — Quick relief.
-
Cons — Side effects, no root cause fix.
See why long-term medication may fail in TMJ Relief: Why Traditional Treatments Fail.
DIY Remedies and Natural Treatments for Jaw Pain
Options worth trying:
-
Magnesium glycinate.
-
Warm compresses.
-
Soft diet during flare-ups.
Explore more in Alternative TMJ Treatments You Can Try at Home.
How to Prevent Chronic Jaw Pain Recurrences
-
Use a Reviv Mouthguard at night.
-
Maintain good posture.
-
Avoid gum chewing.
-
Get monthly check-ins.
Success Stories: Managing Chronic Jaw Pain
I’ve seen people go from daily migraines to pain-free in 90 days by:
-
Identifying triggers.
-
Using precision-fit guards.
-
Doing daily mobility work.
FAQs
1. Can jaw pain be caused by anxiety? — Yes, via clenching.
2. Does jaw pain always mean TMJ disorder? — No.
3. Will a mouthguard stop chronic jaw pain? — Often, yes.
4. How long to heal? — Weeks to months.
5. Heat or ice? — Ice for inflammation, heat for tension.
6. Can posture cause jaw pain? — Yes.
7. Avoid chewy foods? — Yes during flare-ups.
8. Can jaw pain cause headaches? — Absolutely.
9. Is surgery good for TMJ? — Only last resort.
10. Does TMJ pain go away on its own? — Sometimes, but not always.
Conclusion
Chronic jaw pain is rarely “just stress.”
It’s a combination of mechanical, muscular, and lifestyle factors.
Identify the root cause early to save years of trial and error.
If you want a proven, non-invasive fix, try the Reviv Mouthguard here.