TMJ, Tinnitus, and Ear Pain: What’s the Connection and Where a Mouthguard Fits
Share
1. What Is TMJ Disorder?
TMJ disorder happens when the hinge connecting your jaw to your skull doesn’t work smoothly.
It can cause:
-
Jaw clicking or popping
-
Pain when chewing
-
Tension headaches
For more on jaw mechanics, see our blog post: How Jaw Alignment Impacts Sleep: The Surprising Connections.
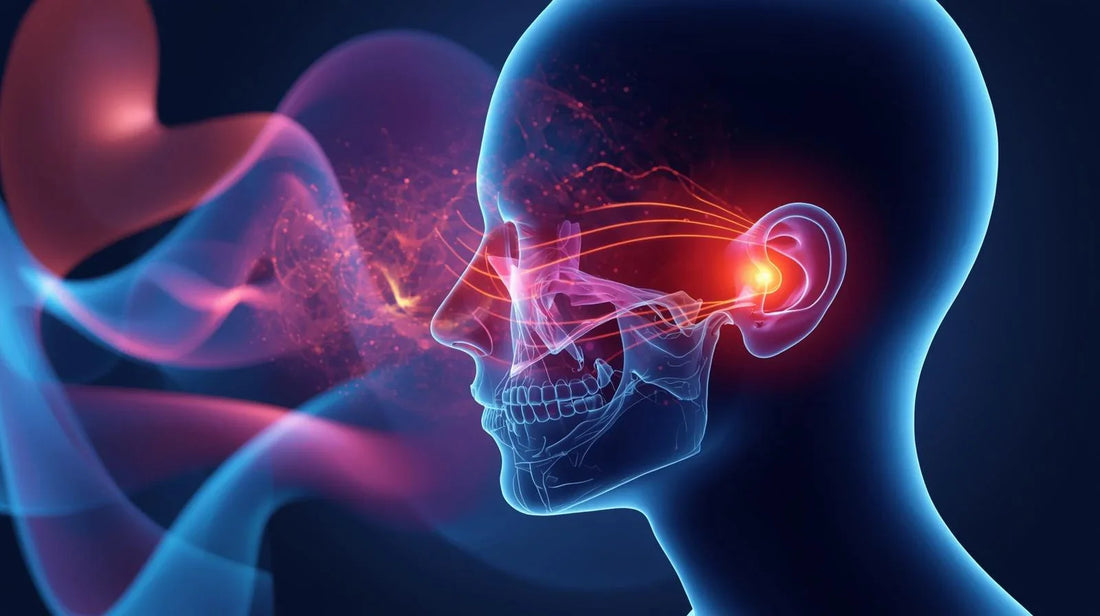
2. How TMJ Can Trigger Tinnitus
The ear and jaw share nerves and muscles.
When TMJ is irritated, it can overstimulate the auditory nerve, causing ringing or buzzing in the ears.
3. The Overlap Between Ear Pain and TMJ Dysfunction
Many people think they have an ear infection.
But the pain often comes from jaw joint inflammation spreading into ear structures.
4. Why Dentists and ENTs Often Disagree
An ENT might say “no infection.”
A dentist might say “jaw misalignment.”
Both can be true.
The medical system treats symptoms in silos. That’s why patients get stuck in the loop.
5. The Role of Bruxism (Teeth Grinding)
Night grinding is a hidden culprit.
Constant grinding stresses the TMJ, leading to both jaw and ear issues.
For more on teeth grinding, see our blog post: Best Home Remedies and Exercises for TMJ Pain Relief.
6. Can a Mouthguard Help With Tinnitus?
Yes—indirectly.
A well-fitted mouthguard reduces clenching and muscle tension.
Less tension = less irritation of the ear nerves.
7. Why Over-the-Counter Mouthguards Often Fail
Cheap boil-and-bite guards protect teeth but don’t fix jaw alignment.
If alignment is the root cause, OTC guards can even make symptoms worse.
See Custom vs Over-the-Counter TMJ Mouth Guards: Pros, Cons, and What Actually Works.
8. The Science of Ear Pressure and Jaw Alignment
The TMJ sits just millimeters from the ear canal.
Even small shifts in jaw position change how pressure is distributed, leading to blocked or “full” ear sensations.
9. Stress, TMJ, and Ear Pain: The Unholy Trio
Stress → clenching.
Clenching → jaw tension.
Jaw tension → ear pain and tinnitus.
Breaking that cycle often requires both physical and behavioral fixes.
Read: TMJ vs Stress: How to Tell the Difference & What Actually Works.
10. Why Traditional Medicine Often Misses TMJ-Ear Links
Doctors may overprescribe antibiotics for “ear infections.”
But if no bacteria are present, the meds do nothing.
A contrarian view: jaw rehab should come before drugs.
11. Mouthguards vs. Splints: What’s the Difference?
Splints reposition the jaw.
Mouthguards mostly protect teeth.
Reviv Mouthguard is designed with jaw stability in mind—bridging that gap.
See: Reviv TMJ Mouth Guard: The Expert’s Guide to Buying the #1 Solution for Jaw Pain.
12. Can TMJ Cause Dizziness Too?
Yes.
The same nerves that connect jaw and ear also impact balance.
If you’ve felt vertigo with jaw pain, it’s not in your head—it’s in your jaw.
13. The Hidden Cost of Ignoring TMJ-Ear Pain
-
Chronic ringing
-
Hearing issues
-
Constant pain
These can escalate into anxiety, sleep disruption, and even depression.
14. My Personal Experiment With a Mouthguard
When I first wore a properly fitted guard, I expected “teeth protection.”
Instead, I noticed less ringing in my ears after just two weeks.
That’s when I realized how much jaw pressure was driving my ear issues.
See Exclusive Buyer’s Review: Why Reviv TMJ Mouth Guard Is Worth Every Dollar.
15. Foods That Make TMJ and Tinnitus Worse
-
Chewy steaks
-
Gum
-
Crunchy snacks
If you’re in pain, these are silent amplifiers.
For more, check out: The TMJ Diet: Foods That Help Reduce Inflammation and Pain.
16. Exercises That Ease Jaw-Ear Tension
Try:
-
Gentle jaw stretches
-
Tongue-to-palate resting posture
-
Heat packs before bed
For more on posture and TMJ, see: TMJ, Posture, and Whole-Body Alignment: What’s the Connection?.
17. How Sleep Quality Impacts TMJ and Ear Pain
Poor sleep → more clenching.
Mouthguards protect you while you sleep, breaking the cycle.
See: How to Improve Sleep Quality With Oral Appliance Therapy.
18. The Role of Posture in Jaw and Ear Health
Slouched posture shifts jaw alignment.
That shift puts more strain on the TMJ, worsening ear symptoms.
See: How to Use Dental Biomechanics to Improve Your Posture.
19. When to See a Professional
If pain lasts more than 2–3 weeks, don’t wait.
A dentist familiar with TMJ can evaluate if a custom guard is needed.
Learn: Are Custom Mouthguards Effective for TMJ Relief?.
20. Why Reviv Mouthguard Fits Into the Solution
Unlike generic guards, Reviv is designed for TMJ relief, not just tooth protection.
It supports jaw stability while reducing grinding forces—helping with tinnitus and ear pain too.
See: Shop Reviv TMJ Mouth Guard: The Smart Buyer’s Route to Pain-Free Living.
FAQs
1. Can TMJ really cause ringing in the ears?
Yes, because of shared nerves between the jaw and ear.
2. Do mouthguards cure tinnitus?
Not directly. But they reduce jaw tension, which can lessen symptoms.
3. Why does my ear hurt with no infection?
Likely referred pain from the TMJ.
4. Can TMJ problems affect hearing?
Yes. Chronic tension can muffle sounds or create fullness.
5. Will my tinnitus go away if I fix my jaw?
It depends. Some see total relief, others partial improvement.
6. Is stress management important for TMJ?
Absolutely. Stress drives clenching, the #1 trigger.
7. Can poor posture make tinnitus worse?
Yes, by misaligning the jaw.
8. Should I avoid OTC night guards?
If symptoms are severe, yes. Go for a TMJ-focused design.
9. How long before a mouthguard helps?
Some people feel relief in 1–2 weeks. Others take longer.
10. Is Reviv Mouthguard worth it?
If you want both protection and jaw stability, it’s a smart investment.
Conclusion
TMJ, tinnitus, and ear pain are connected by nerves, muscles, and stress cycles most doctors overlook.
A properly designed mouthguard, like Reviv, can reduce grinding, stabilize the jaw, and ease ear symptoms naturally.
If you’ve tried everything else, it may be time to test what works while you sleep.
👉 Buy Reviv Mouthguard today by clicking Here.